Glycemic index
|
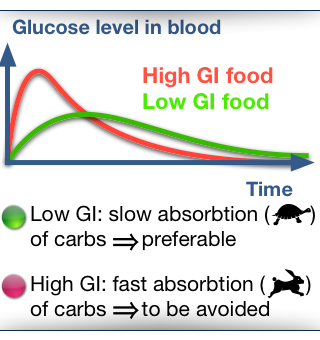
Carbs in foods are metabolized at different rate, represented by different Glycemic Index (GI), from the fastest absorption (GI = 140), moderate rate like bread (GI = 100), to very slow absorption (e.g., beans). For diabetics, high GI will lead to an rapid increase of the blood glucose.
Diets based on low GI foods seems to lead to a decrease of risk to develop a type 2 diabetes [6]. |
Is this index reliable?
Measuring GIs is in practice a very difficult task, because carbs are metabolized in a very different way from people to people. To limit the uncertainties, measures are repeated and averaged, making this measure very costly. By the way, only a fraction of standard foods items are currently measured (less than 1000). CaloriesMinute replace unavailable GIs by measures done on similar (although not exactly equivalent) foods items, or food of same composition.
Glycemic index for meals
|
A meal GI is the sum of all components GI, weighted by the carbs of the component divided by the total quantity of carbs in the meal. It is therefore no more than a simple weighted "average" of GIs. This meal GI is correlated to the measured GIs [7]. It is thus a way to estimate your meal GI, if no other measure exists. This average is given by the rabbit and the turtle in the title:
|
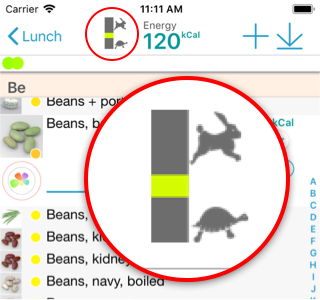
How to activate Glycemic Index in Calories Minute?
From the from page, select "Profile and settings", and "Interface", and then "Show Glycemic Index". The title now contains the average GI for the selected foods. The GI is also indicated for every food item by a small colored dot on food picture (red: high GI, green: low GI, blank: no carbs). Average Glycemic Index and Glycemic Load is also provided in the Graphics / Flower page.